DDB
Returns the depreciation of an asset for a given year using the double (or other factor) declining-balance method.
Syntax:
DDB(originalcost, salvagevalue, lifetime, year, factor)
originalcost: the initial cost of the asset.
salvagevalue: is the value at the end of the depreciation (sometimes called the salvage value of the asset).
lifetime: the number of years over which the asset is being depreciated.
year: the year number for which the depreciation is calculated.
factor: the factor to set the depreciation rate (2 if omitted).
To calculate depreciation, DDB uses a fixed rate. When factor = 2 this is the double-declining-balance method (because it is double the straight-line rate that would depreciate the asset to zero). The rate is given by:
rate = factor / lifetime.
The depreciation each year is calculated as
MINIMUM( book_value_at_start_of_year * rate; book_value_at_start_of_year - salvagevalue )
Thus the asset depreciates at rate until the book value is salvagevalue.
Example:
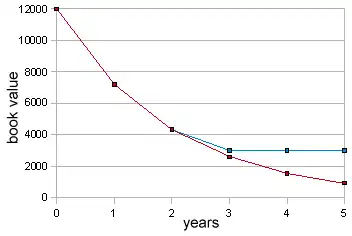
DDB(12000, 3000, 5, 1)
returns 4800 in currency units. The rate is 2/5, or 40%. The book value at the start of year 1 is 12000, and 40% of 12000 is 4800.
DDB(12000, 3000, 5, 2)
returns 2880 in currency units. The book value at the start of year 2 is 12000 - 4800 = 7200, and 40% of 7200 is 2880.
DDB(12000, 3000, 5, 3)
returns 1320 in currency units. The book value at the start of year 3 is 7200 - 2880 = 4320; and 40% of 4320 is 1728 - but DDB returns only enough depreciation to reduce the book value to the salvage value - that is 4320 - 3000 = 1320.
DDB(12000, 3000, 5, 4)
returns 0 in currency units. The book value at the start of year 4 is equal to the salvage value; no further depreciation is possible.
Application:
A Business Truck
Let's imagine a small business, "Green Gardens Landscaping," purchases a new commercial truck for their operations.
- Cost: The initial cost of the truck is $50,000.
- Salvage: The company estimates that after 5 years, the truck will be worth $10,000 as a trade-in or for scrap.
- Life: The useful life of the truck is 5 years.
Here is a table showing the depreciation calculation for each year using the DDB function.
Year | DDB Function | Depreciation Expense | Beginning Book Value | Accumulated Depreciation | End-of-Year Book Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
A | B | C | D | E | F | ||
1 | 1 | DDB(50000, 10000, 5, 1) | $20,000.00 | $50,000.00 | $20,000.00 | $30,000.00 | |
2 | 2 | DDB(50000, 10000, 5, 2) | $12,000.00 | $30,000.00 | $32,000.00 | $18,000.00 | |
3 | 3 | DDB(50000, 10000, 5, 3) | $7,200.00 | $18,000.00 | $39,200.00 | $10,800.00 | |
4 | 4 | DDB(50000, 10000, 5, 4) | $800.00 | $10,800.00 | $40,000.00 | $10,000.00 | |
5 | 5 | DDB(50000, 10000, 5, 5) | $0.00 | $10,000.00 | $40,000.00 | $10,000.00 |
Explanation of the Table:
- Year 1: The DDB function calculates the depreciation expense for the first year. The depreciation is based on the initial book value ($50,000). The formula essentially calculates a depreciation rate (which is 2 / 5 or 40%) and applies it to the beginning book value ($50,000 * 40% = $20,000).
- Year 2: The depreciation for the second year is calculated on the new book value ($30,000). So, $30,000 * 40% = $12,000.
- Year 3: The depreciation is calculated on the book value at the start of year 3 ($18,000). So, $18,000 * 40% = $7,200.
- Year 4: The calculated depreciation for this year ($10,800 * 40% = $4,320) would cause the book value to fall below the salvage value of $10,000. The DDB method will automatically adjust the depreciation in the final periods so that the ending book value is exactly the salvage value. In this case, the depreciation is limited to the amount needed to bring the book value down to $10,000 ($10,800 - $10,000 = $800).
- Year 5: Since the book value is already at the salvage value of $10,000 at the end of year 4, no further depreciation is recognized.
As you can see from the table, the depreciation expense is much higher in the first two years and significantly decreases in the later years, accurately reflecting the higher productivity and value loss of a new truck and its eventual decline in performance.
PRODUCT & FEATURES
RESOURCES
Terms | Privacy | Spam Policy
© 2026 Zapof