FREQUENCY
Returns an array, categorising values of a data set into given intervals.
Syntax:
FREQUENCY(data, bins)
data is a range or array containing numerical data.
bins is a single column range or array containing numbers in ascending order which are the upper limit of each category.
FREQUENCY returns a single column array, where the first element is the count of values in data that are less than or equal to the first value in bins, the second value is the count of values in data that are greater than the first value but less than or equal to the second value in bins, and so on. The array returned is one element longer than bins; the last element contains the count of values in data that are greater than the last value in bins.
Example:
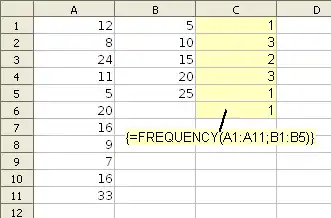
FREQUENCY(A1:A11, B1:B5)
when entered as an array formula, where the data values in A1:A11 are 12,8,24,11,5,20,16,9,7,16,33 and the values in B1:B5 are 5,10,15,20,25 returns {1|3|2|3|1|1}. The first value is the count of data values less than or equal to 5, and the last value is the count of data values greater than 25.
Application:
Analyzing Student Test Scores
Scenario: A teacher wants to analyze the distribution of scores on a recent math test for a class of 20 students. They want to see how many students fall into specific score ranges.
Data: The scores of the 20 students are as follows:
Student | Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|
A | B | ||
1 | Student 1 | 75 | |
2 | Student 2 | 82 | |
3 | Student 3 | 91 | |
4 | Student 4 | 68 | |
5 | Student 5 | 88 | |
6 | Student 6 | 95 | |
7 | Student 7 | 78 | |
8 | Student 8 | 62 | |
9 | Student 9 | 85 | |
10 | Student 10 | 73 | |
11 | Student 11 | 90 | |
12 | Student 12 | 80 | |
13 | Student 13 | 77 | |
14 | Student 14 | 93 | |
15 | Student 15 | 65 | |
16 | Student 16 | 89 | |
17 | Student 17 | 70 | |
18 | Student 18 | 98 | |
19 | Student 19 | 81 | |
20 | Student 20 | 76 |
Goal: The teacher wants to group the scores into the following ranges:
- Scores from 0 to 69
- Scores from 70 to 79
- Scores from 80 to 89
- Scores from 90 to 100
Using the FREQUENCY function:
- Define the Data Array (data): This is the range containing the student scores. Let's say the scores are in cells B1:B20.
- Define the Bins Array (bins): This array contains the upper limit of each category. Remember, the FREQUENCY function counts items up to and including the bin value. The bins should be in ascending order.
The bins for our example would be:
Let's place these bin values in another table. - 69 (for scores up to 69)
- 79 (for scores up to 79)
- 89 (for scores up to 89)
- 100 (for scores up to 100)
Bins (Upper Limits) | ||
|---|---|---|
A | ||
1 | 69 | |
2 | 79 | |
3 | 89 | |
4 | 100 |
- Applying the FREQUENCY function:
- Enter the following formula: FREQUENCY(B1:B20 from the first table, A1:A4 from the second table)
Results:
The FREQUENCY function will return an array of values into the selected cells, which represents the count for each category.
Category | Count | ||
|---|---|---|---|
A | B | ||
1 | Scores 0-69 | 3 | |
2 | Scores 70-79 | 6 | |
3 | Scores 80-89 | 6 | |
4 | Scores 90-100 | 5 | |
5 | More than 100 | 0 |
Result for FREQUENCY(B1:B20 from the first table, A1:A4 from the second table):
Explanation of the Output:
- Bin 69: The function counts all scores less than or equal to 69. The scores are 68, 62, and 65. The count is 3.
- Bin 79: The function counts all scores greater than 69 and less than or equal to 79. The scores are 75, 78, 73, 77, 70, and 76. The count is 6.
- Bin 89: The function counts all scores greater than 79 and less than or equal to 89. The scores are 82, 88, 85, 80, 89, and 81. The count is 6.
- Bin 100: The function counts all scores greater than 89 and less than or equal to 100. The scores are 91, 95, 90, 93, and 98. The count is 5.
- Bin More than 100: This final cell is a special feature of the FREQUENCY function. It counts any values that are greater than the last bin (in this case, scores greater than 100). Since there are no scores above 100, the count is 0.
This example demonstrates how the FREQUENCY function quickly creates a frequency distribution or a histogram, which is useful for summarizing large datasets and understanding their characteristics.
PRODUCT & FEATURES
RESOURCES
Terms | Privacy | Spam Policy
© 2026 Zapof