GAMMA
Returns the values of the Gamma function.
Syntax
GAMMA(x)
x is a number.Constraint: If x is an integer, then x must be positive.
Semantic
GAMMA(x) calculates
Example
GAMMA(4) = 6.0 exact
GAMMA(34.56) ≈ 6.2336323276E+037
GAMMA(−4) not defined
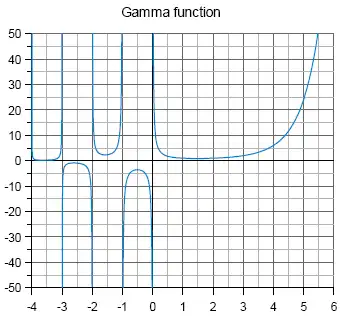
Remarks
For x < 0.5 Eulers reflection formula is used.
The Gamma function has poles for negative integers and for zero. Near the poles the values are less accurate.
If x is a positive integer, then
Application:
Calculating the Probability of a Capacitor's Lifetime
Suppose the lifetime of a capacitor is modeled by a Gamma distribution with a shape parameter α=3 and a rate parameter β=0.5. We want to calculate the probability density at a specific lifetime, say x=5 years.
First, we need to calculate the value of the Gamma function for α=3, which is (3). Since 3 is an integer, (3)=(3−1)!=2!=2.
Now we can substitute the values into the PDF equation:
This value, 0.128, represents the probability density at a lifetime of 5 years.
The Role of the Gamma Function in the Calculation
The Gamma function is essential for calculating the normalization constant, , which ensures that the total area under the probability density curve is exactly 1. Without this normalization, the function would not be a valid probability distribution.
The following table shows how the value of the Gamma function changes with its parameter x:
x | Gamma(x) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
A | B | ||
1 | 1 | 1 | |
2 | 2 | 1 | |
3 | 3 | 2 | |
4 | 4 | 6 | |
5 | 5 | 24 | |
6 | 1.5 | 0.8862 | |
7 | 2.5 | 1.3293 | |
8 | 3.5 | 3.3234 |
As you can see from the table, for integer values of x, the Gamma function is simply the factorial of (x-1). However, for non-integer values (like 1.5, 2.5, and 3.5), the Gamma function provides a continuous and meaningful result, which is crucial for modeling continuous variables like the lifetime of a capacitor. This is a key reason why the Gamma function is used in the Gamma distribution, allowing it to model a wide range of real-world phenomena.
PRODUCT & FEATURES
RESOURCES
Terms | Privacy | Spam Policy
© 2026 Zapof