ZTEST
Returns the result of a z-test.
Syntax:
ZTEST(data, μ, σ)
data is a range or array containing a random sample from a population (population assumed to have a normal distribution).
μ is the (known) mean of the population.
σ is the (known) standard deviation of the population. If omitted, it is estimated from the sample data by STDEV(data).
ZTEST calculates the z statistic:
where m is the sample mean and n the number in the sample. When the mean and standard deviation of the population are known, the z statistic forms a standard normal distribution - that is, a normal distribution with mean=0 and standard deviation=1.
ZTEST returns the one-sided cumulative probability - the area under the standard normal curve to the right of the z value (shaded blue here):
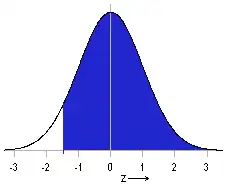
Example:
ZTEST(A2:A20, 9, 2)
returns the result of a z-test on a sample A2:A20 drawn from a population with known mean 9 and known standard deviation 2.
Application:
Testing the Average Weight of Cereal Boxes
Scenario: A cereal company, "Grain Goodness," claims that their large-size cereal boxes have an average net weight of 550 grams. The company's quality control department knows from historical data that the population standard deviation of the box weights is 15 grams. A consumer advocacy group suspects that the actual average weight is less than 550 grams. To test this claim, they randomly select a sample of 30 cereal boxes from various stores and weigh them.
Hypotheses:
- Null Hypothesis (H0): The true mean weight of the cereal boxes is 550 grams (μ=550).
- Alternative Hypothesis (Ha): The true mean weight of the cereal boxes is less than 550 grams (μ<550).
Given Parameters:
- Population Mean (μ): 550 grams (the company's claim)
- Population Standard Deviation (σ): 15 grams (known from historical data)
- Sample Size (n): 30
Sample Data:
The consumer group weighs the 30 cereal boxes and records the following weights (in grams):
Box | Weight (g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
A | B | ||
1 | 1 | 545 | |
2 | 2 | 538 | |
3 | 3 | 552 | |
4 | 4 | 540 | |
5 | 5 | 548 | |
6 | 6 | 555 | |
7 | 7 | 530 | |
8 | 8 | 544 | |
9 | 9 | 539 | |
10 | 10 | 551 | |
11 | 11 | 547 | |
12 | 12 | 541 | |
13 | 13 | 536 | |
14 | 14 | 543 | |
15 | 15 | 550 | |
16 | 16 | 549 | |
17 | 17 | 550 | |
18 | 18 | 542 | |
19 | 19 | 535 | |
20 | 20 | 547 | |
21 | 21 | 540 | |
22 | 22 | 551 | |
23 | 23 | 543 | |
24 | 24 | 548 | |
25 | 25 | 546 | |
26 | 26 | 537 | |
27 | 27 | 549 | |
28 | 28 | 553 | |
29 | 29 | 545 | |
30 | 30 | 541 |
Using the ZTEST Function:
When you input the sample data into the ZTEST function with the parameters data (the range of the 30 weights), μ (550), and σ (15), the function returns a value of 0.977695141.
This value is the one-tailed p-value, but it represents the probability of a sample mean being greater than the one you observed. Since our alternative hypothesis is that the mean is less than 550 grams, we are conducting a left-tailed test.
To find the correct p-value for our left-tailed test, we must subtract the ZTEST result from 1.
Calculating the Correct P-Value:
- P-value = 1−0.977695141
- P-value = 0.022304859
Conclusion:
- A common significance level (α) for hypothesis testing is 0.05.
- We compare our calculated p-value to the significance level: 0.0223 < 0.05.
- Since the p-value is less than the significance level, we reject the null hypothesis.
This result provides statistically significant evidence to support the consumer group's claim that the average weight of the "Grain Goodness" large-size cereal boxes is less than the claimed 550 grams.
Result for ZTEST:
Result for P-value:
PRODUCT & FEATURES
RESOURCES
Terms | Privacy | Spam Policy
© 2026 Zapof